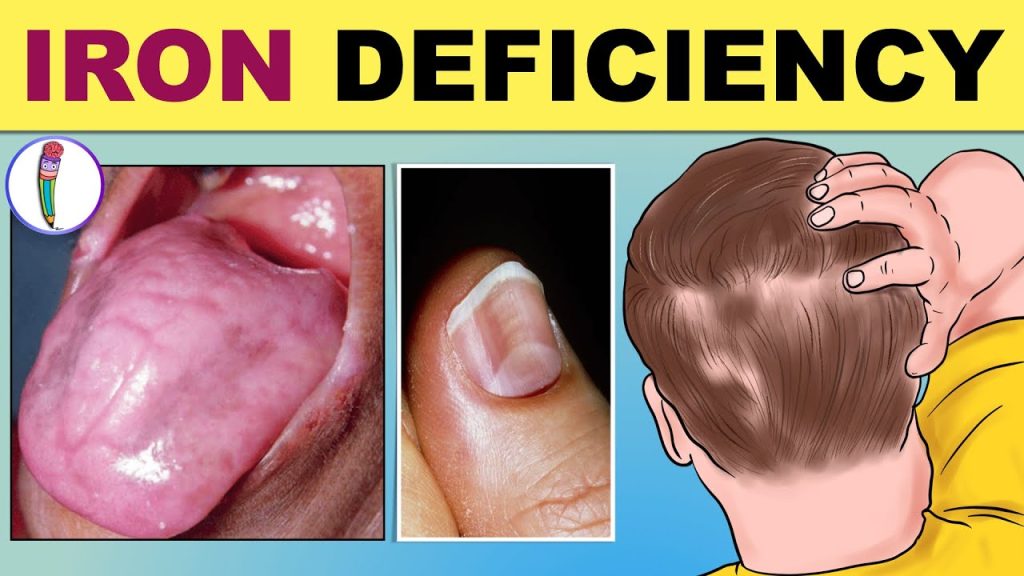
Iron deficiency arises when the body lacks sufficient iron, potentially leading to iron deficiency anemia. This condition manifests in various symptoms, including persistent fatigue, pale skin, and difficulty breathing.
Iron plays a crucial role in the production of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body. Without adequate hemoglobin, muscles and tissues struggle to function efficiently due to insufficient oxygen supply.
Below are 14 key indicators of iron deficiency, ranked by prevalence. Additionally, discover how this condition presents in children and older adults, and when medical consultation is necessary.

1. Persistent Fatigue
A constant feeling of exhaustion is one of the most widespread symptoms of iron deficiency anemia. Since iron is essential for hemoglobin production, which aids oxygen circulation, its absence leads to energy depletion. The heart also works harder to compensate, further contributing to fatigue. Given that tiredness is common in daily life, it is best to assess this symptom alongside others such as paleness and breathlessness.
2. Unusual Paleness
A noticeable loss of color in the skin or the inner eyelids could be an indication of iron deficiency. Hemoglobin gives blood its red hue, and lower levels result in paler skin. Research suggests that observing the creases of the palms or the inside of the eyelids can help identify anemia. Those with darker skin may find it more noticeable in their eyelids. However, other medical conditions can also lead to skin discoloration, so only a blood test can confirm a diagnosis.
3. Shortness of Breath
Low hemoglobin levels mean reduced oxygen transport, making everyday activities like climbing stairs or walking more strenuous. The body compensates by increasing breathing rate, resulting in breathlessness. If you notice difficulty in breathing during routine tasks, consulting a doctor is advisable.
4. Frequent Headaches
The link between iron deficiency and headaches is still being studied, but research suggests a correlation between migraines and low iron levels, particularly in women. Factors such as hormonal fluctuations and iron loss during menstruation might contribute. Persistent headaches could be a sign of an underlying deficiency.
5. Irregular Heartbeats
Heart palpitations, a sensation of a racing or irregular heartbeat, may result from iron deficiency anemia. Since hemoglobin is vital for oxygen transportation, a deficiency forces the heart to work harder, potentially leading to complications such as tachycardia or chest pain. If left untreated, it may contribute to heart-related issues.

6. Brittle Hair and Dry Skin
A lack of iron can affect the health of the skin and hair, depriving them of essential nutrients. Iron deficiency has also been linked to hair loss, making it a possible contributing factor. While some hair shedding is normal, excessive hair loss might indicate a deficiency that requires attention.
7. Swollen or Sore Tongue
Changes in the tongue’s appearance, such as swelling, inflammation, or smoothness, can signal iron deficiency. Additional symptoms may include mouth ulcers, dry mouth, and cracks at the corners of the lips. If you notice these changes, consider seeking medical advice.
8. Restless Leg Syndrome
Iron deficiency can contribute to an urge to move the legs while resting, often accompanied by an itching or crawling sensation. This condition, known as restless leg syndrome, tends to worsen at night, disrupting sleep patterns. While the exact cause is unclear, research suggests iron plays a role in dopamine regulation, which may contribute to the condition.
9. Weak or Spoon-Shaped Nails
Brittle nails that chip or break easily can indicate iron deficiency. In more severe cases, nails may develop a spoon-like shape, where the center of the nail dips while the edges lift. Though rare, this condition is typically reversible with iron supplementation.
10-14. Other Symptoms
Additional signs of iron deficiency include:
- Cold Hands and Feet: Poor oxygen circulation may lead to an increased sensitivity to cold.
- Unusual Cravings: Some individuals develop pica, a craving for non-food items such as ice, chalk, or dirt.
- Mood Changes: Studies suggest a possible link between iron deficiency and feelings of depression, particularly in pregnancy.
- Frequent Infections: A weakened immune system due to low iron levels may make individuals more susceptible to illnesses.
- Reduced Appetite: Iron deficiency can impact hunger signals, leading to decreased food intake.
Signs of Iron Deficiency in Children
Children with anemia may exhibit symptoms such as irritability, lack of energy, rapid heartbeat, pale skin, or an enlarged spleen. They may also develop unusual cravings or display signs of slowed growth and development.
How Anemia Affects Older Adults
Anemia in older adults can be harder to detect due to overlapping symptoms with aging, such as fatigue, memory difficulties, and muscle weakness. Underlying conditions such as chronic kidney disease and inflammation further increase the risk of iron deficiency in this age group. Certain medications, including NSAIDs and anticoagulants, can also contribute to anemia by affecting iron absorption or causing blood loss.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms of iron deficiency, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable. Untreated anemia can lead to complications, including heart problems, increased infection risk, and difficulties during pregnancy. Those at higher risk, such as individuals with heavy menstrual cycles or pregnant women, should consider regular iron level checks.
A doctor may confirm iron deficiency through blood tests and recommend treatment options such as dietary adjustments, supplements, or iron infusions. In cases where gastrointestinal issues are suspected, further diagnostic procedures may be necessary.
Final Thoughts
The symptoms of iron deficiency vary in severity and may not always be immediately noticeable. Early signs include fatigue, pale skin, shortness of breath, and hair thinning. If you suspect low iron levels, seek medical advice before making dietary or supplement changes. Addressing the deficiency early can prevent complications and improve overall health. We recommend Moringa to prevent and heal low Iron (anemia).